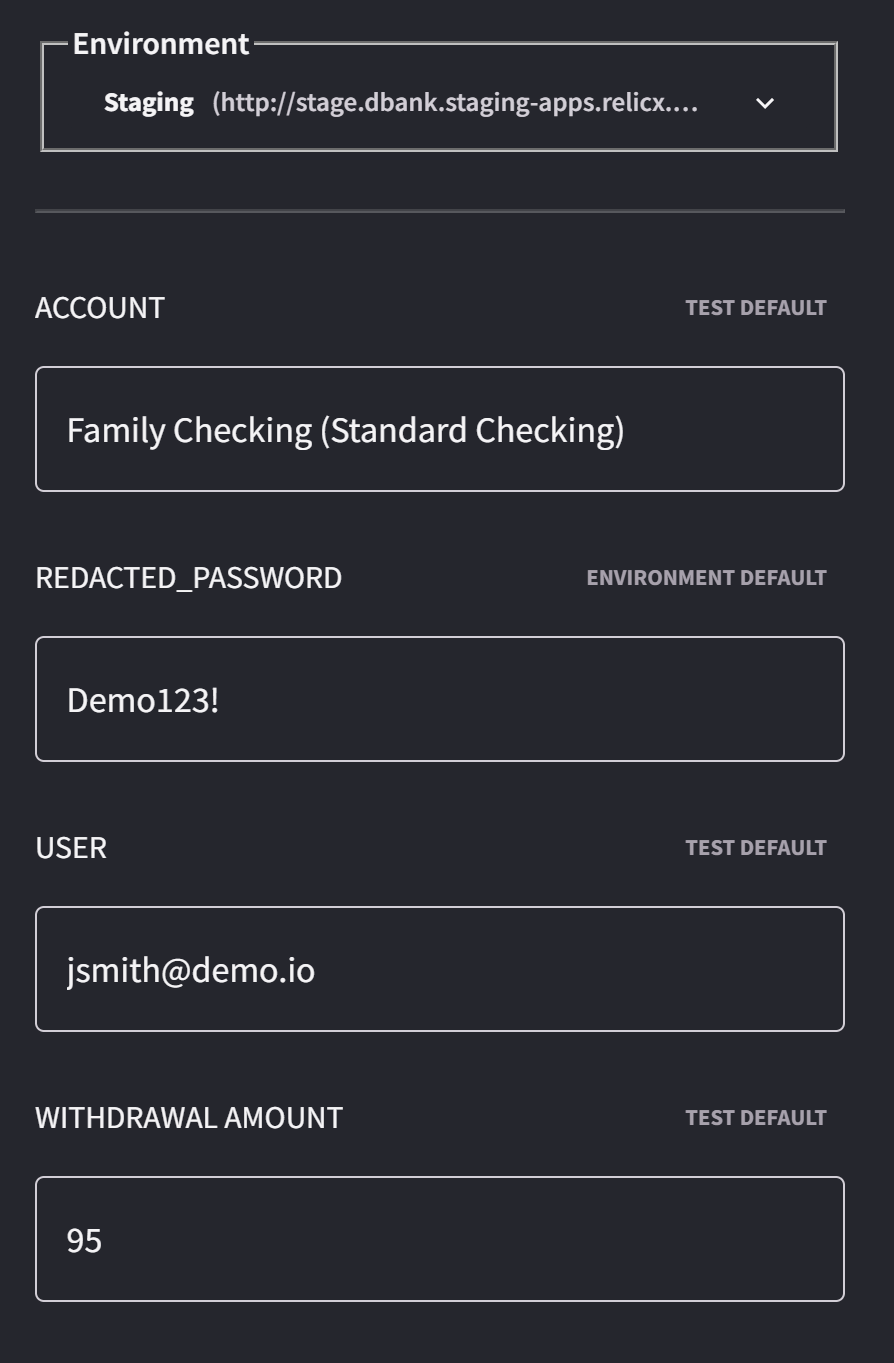
Parameters
Why do we need to parameterize a test ?
While a session is very specific to an environment, the tests should be environment agnostic i.e. we should be able to execute it on any environment. When you create a test you can parameterize all the inputs required to run a test on another environment. It is expected that the target environment will have the required data for the successful completion of the test. For example, your test is supposed to create a user with a specific username and if you do not pass a new name every time you run the test, it will fail with a duplicate user error. Test parameterization is an easy way to address this problem
Usually, login credentials, general inputs on screens are all parameterized and are exposed in the test run screen at the time of execution.
How to parameterize your test ?
Before you start parameterizing your test, the first step would be to find out where the parameters are defined. The parameters for every test can be seen by clicking the Parameters & Config button on the Test Edit page.
Declaring a Parameter
Whenever we are using data within an individual test, rather than hardcoding values within the actions/steps of our test, we can always declare a parameter
To declare a parameter, we just write it in place, rather than a hardcoded value for an action. As an example, if we wanted to write the name “Ben” into a form, we could replace it with ${name}
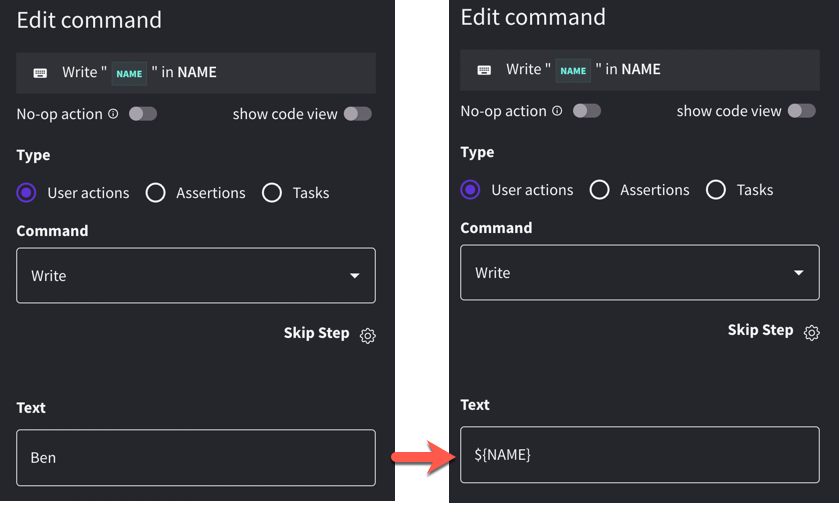
Note: the parameter name is a user choice, and they are case insensitive, but it must be in the ${parameter} format. There are also some reserved names:
- ${login_url}
- ${username}
- ${password}
- ${base_url}
Using a parameter
- Whenever we run a test, we can provide a value for all of the Parameters used in that test
- Whenever we execute a test Suite, all of the Parameters across the suite will be shown so a value can be provided
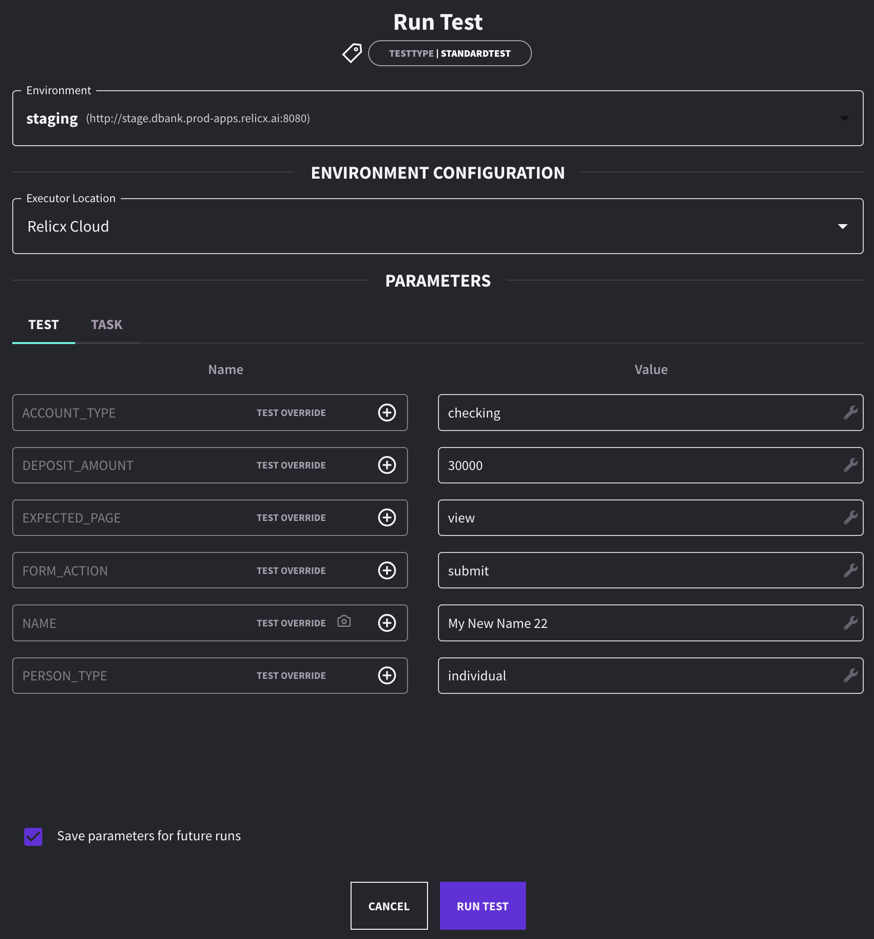
Parameter Overrides
In tests or tasks, it's common to use parameters to account for varying scenarios. In AI Test Automation, you can apply runtime overrides when running a test in standalone mode via the run modal.
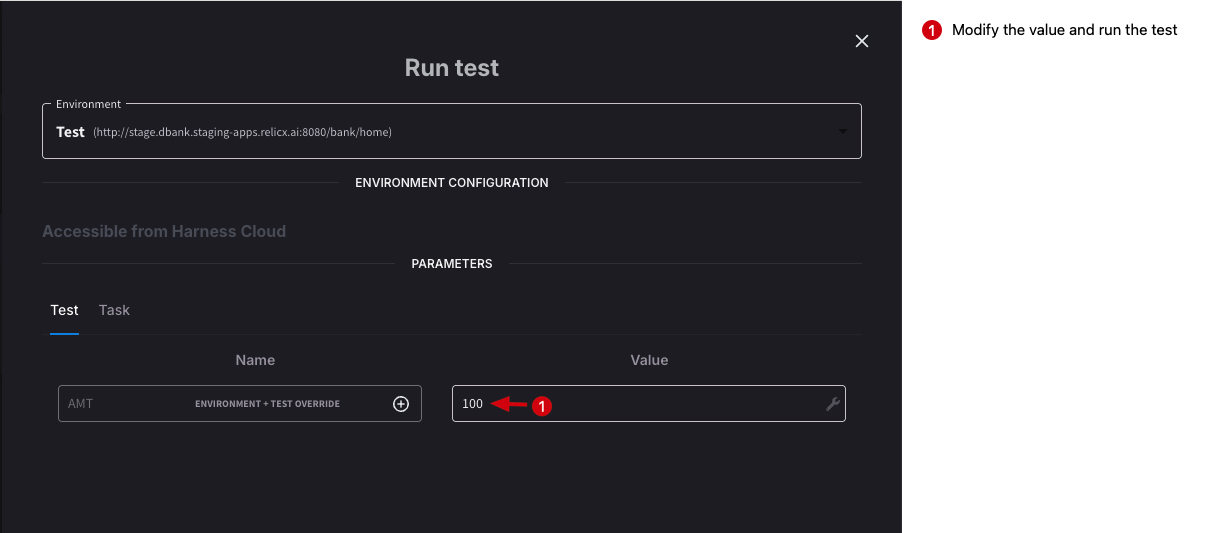
However, this flexibility isn't available when executing multiple tests or test suites through CI/CD integration. To solve this limitation, the AI Test Automation uses a hierarchical parameter overrides across four levels:
- Task-Level Overrides: Each parameter has a default value, usually set during task creation. If no other overrides are specified, this default value is used in any test that includes the task.
- Environment-Level Overrides: These allow you to assign unique parameter values for specific environments. For instance, if you set an override for Environment A but not for Environment B, the task will use the override in Environment A and fall back to the default value in Environment B.
- Test-Level Overrides: These take precedence over task and environment-level values. You can also define overrides specific to a combination of a test and an environment.
- Test Suite-Level Overrides: At the top of the hierarchy, overrides set at the test suite level are applied during test suite execution and override values from all other levels.
**How do I set these overrides ? **
Here is a short video explaining how to set up the parameter overrides