Elastigroup Blue-Green Traffic Shifting Step
Harness supports gradual traffic shifting during Spot Elastigroup Blue-Green deployments by updating AWS ALB listener rules. Similar to ECS deployments, this lets you gradually shift traffic between prod and stage target groups—on the same listener or across multiple listeners—without relying on Auto Scaling Group behavior.
Overview
In Spot Elastigroup Blue-Green deployments, you must define distinct listener rules (or listeners) for prod and stage target groups. During deployment, Harness updates these listener rules to incrementally shift traffic—similar to how ECS Blue-Green traffic shifting works with ALB weighted target groups.
You can configure traffic shifting between target groups attached to the same listener rule, giving you the flexibility to:
- Use multiple target groups in a single rule with configurable traffic distribution across target groups.
- Test new versions incrementally in dev and then production environments.
- Perform gradual roll-outs with approval gates between steps.
- Revert traffic back to the original forward configuration in case of issues.
Key Benefits
- Progressive roll-outs: Shift 10% → 50% → 100% traffic to your new Spot service.
- Safe rollback: Revert to original routing by restoring listener rules.
- Flexible topology: Use either two rules on one listener or two separate listeners.
Set up Elastigroup Blue-Green Traffic Shifting
- Add an Spot stage to your pipeline.
- Add a Harness Spot Elastigroup service in the stage Service. For more information, refer Adding an Elastigroup Service
- Add a Harness AWS environment and infrastructure in the stage Environment. For more information, refer Adding an Elastigroup Environment
- In the Execution strategies tab, select the Blue Green strategy and enable the checkbox Add Traffic Shifting Steps under the Enable Traffic Shifting for Elastigroup Deployment section.
Your Execution tab now includes Elastigroup Blue Green Setup and Elastigroup Blue Green Traffic Shift steps.
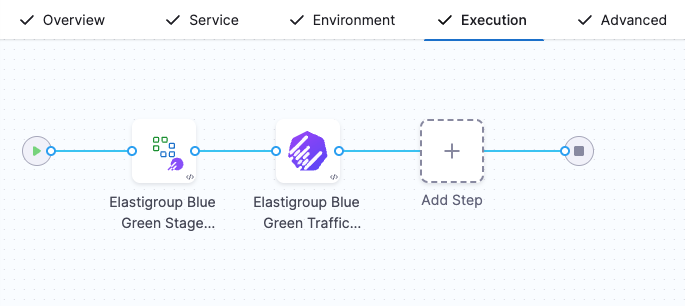
If you do not select the Add Traffic Shifting Steps checkbox, then your execution tab will include Elastigroup Blue Green Setup and Elastigroup Swap Route.
You can also use a blank canvas strategy and manually add the Elastigroup Blue Green Setup and Elastigroup Blue Green Traffic Shift steps to your stage.
In Spot Elastigroup deployments, a single stage can include multiple load balancer configurations. Some load balancers can use traffic shifting—handled by the Elastigroup Blue Green Traffic Shift step—while others can use the traditional Elastigroup Swap Route step. All load balancer configurations are defined through the Elastigroup Blue Green Setup step.
Configure the Elastigroup Blue Green Stage Setup step.
-
Name : Name of the step
-
Timeout : Execution timeout
-
App Name: Enter a name for the Elastigroup app name that Harness will create. For example, you can use Harness expressions, such as
<+project.identifier>_<+service.identifier>_<+env.identifier>_basic2. You can select a fixed value, runtime input, or expression for this field. -
In Instances, select:
- Same as already running instances: Replicate the already running instances.
- Fixed: Enter Min Instances, Max Instances, and Desired Instances.
-
In Connected Cloud Provider, specify the AWS connector and region to use for this deployment. This configuration is not inherited from the service or infrastructure definition. You must explicitly define the AWS connector and region in this step.
-
In AWS Load Balancer Configuration, select Add to add the ELB configuration/ edit the existing configuration:
- AWS Load Balancer: Select the load balancer to use.
Select the checkbox Use Shift Traffic to enable the Elastigroup Blue Green Traffic Shift to the ELB listener
-
Prod Listener: Select the AWS Application Load Balancer (ALB) listener you want to use for production traffic.
-
Prod Listener Rule ARN: Select the listener rule that forwards traffic to both the production and stage target groups. This rule supports weighted target group configurations for traffic shifting.
-
Stage Target Group ARN: Select the target group where the new version of your service will be deployed during the Blue-Green rollout.
The specified listener rule must reference exactly two target groups: one for the existing (production) service and one for the new (stage) service. This field identifies the stage target group in that rule.

If the Use Shift Traffic checkbox is not selected for any of the Load Balancer Configurations, the Elastigroup Blue Green Traffic Shift step will not be included in the pipeline execution flow.
You can have multiple AWS Load Balancer Configuration based on your use-case and and can choose if you want to use traffic shifting step for the ELB listener or not.
Yaml sample for the step
Yaml sample for the step
- step:
name: Elastigroup Blue Green Stage Setup
identifier: Elastigroup_BGSetup
type: ElastigroupBGStageSetup
timeout: 10m
spec:
name: <+project.identifier>_<+service.identifier>_<+env.identifier>
instances:
type: Fixed
spec:
min: 1
max: 1
desired: 1
connectedCloudProvider:
type: AWS
spec:
connectorRef: AWS_Connector
region: us-east-1
loadBalancers:
- type: AWSLoadBalancerConfig
spec:
loadBalancer: myLB
isTrafficShift: true
prodListenerPort: "8080"
prodListenerRuleArn: prodRuleARN
stageTargetGroupArn: stageTargetGroupArn
failureStrategies: []
Configure the Elastigroup Blue Green Traffic Shift step
This step adjusts traffic weights between target groups.
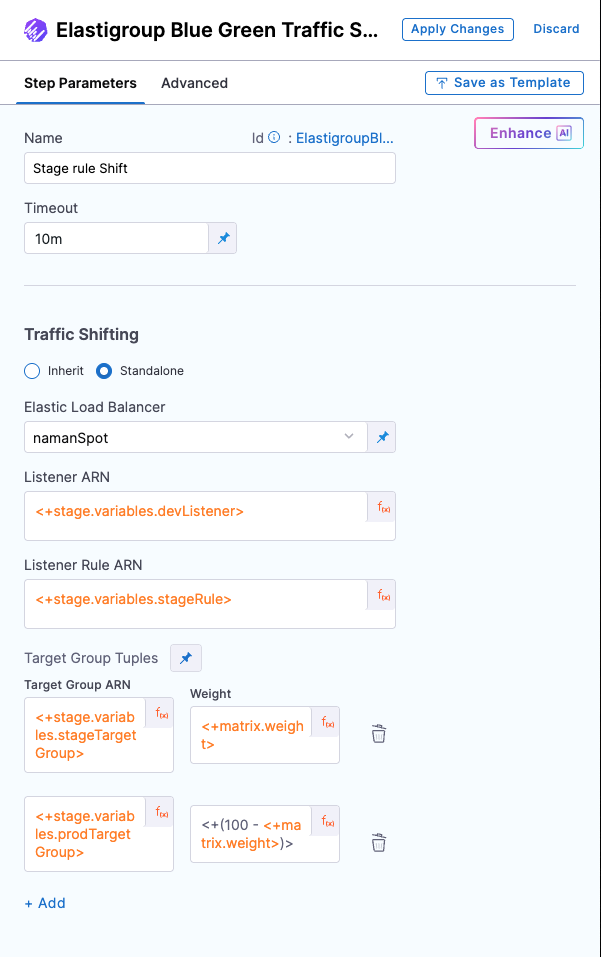
Step parameters
- Name : Name of the step.
- Timeout : Execution timeout.
In the Traffic Shifting configuration, you have the option to either:
- Inherit the configuration from the previous Elastigroup Blue Green Traffic Shift step using the Inherit checkbox, or
- Select the Standalone checkbox to define a new configuration.
Inherit
When Inherit is selected:
- Provide the New Elastigroup Weight.
- Configuration such as Elastic Load Balancer, Listener, and Listener Rule ARN is inherited from the Elastigroup Blue Green Traffic Shift step step.
The step adjusts traffic distribution between the Stage Target Group (where the new service version is deployed) and the Prod Target Group (where the existing version is running):
- Weight
50→ 50% traffic to Stage Target Group, 50% to Prod Target Group. - Weight
70→ 70% to Stage Target Group, 30% to Prod Target Group. - Weight
100→ Suppose you provide the weight as100, the step will route100%traffic to the Stage target group.
At this point, the Inherit step also performs a renaming operation:
- The new (stage) Elastigroup is renamed to match the App Name configured in the Elastigroup Blue Green Traffic Shift step.
- The old (prod) Elastigroup is renamed with a suffix to indicate it’s no longer active.
This renaming only happens when 100% of the traffic has been shifted to the stage target group.
If the weight is less than 100%, the Elastigroup names remain unchanged.
Sample YAML
Sample YAML
- step:
identifier: ElastigroupBlueGreenTrafficShift
type: ElastigroupBlueGreenTrafficShift
name: Elastigroup Blue Green Traffic Shift
timeout: 10m
spec:
elastigroupTrafficShiftWrapper:
type: Inherit
spec:
weightPercentage: <+matrix.weight>
Standalone
When the Standalone checkbox is selected:
- You can provide a new set of Elastic Load Balancer, Listener, and Listener Rule ARN values.
- This allows you to set the forward configuration for the specified listener rule, which defines how traffic is distributed across multiple target groups.
- A common use case is to validate the new service independently in lower environments by referencing the same target groups used in the production rule from the Blue-Green Create step.
You must not reuse the same listener rule that is specified in the Elastigroup Blue Green Traffic Shift step. Doing so will result in a failure during execution.
- Elastic Load Balancer: Click here and select the AWS load balancer to use.
Harness uses the delegate to locate the load balancers and list them in Elastic Load Balancer. If you do not see your load balancer, ensure that the delegate can connect to AWS cluster.
-
Listener ARN: Select the ELB listener to associate with this deployment.
-
Listener Rule ARN: Choose the Listener Rule ARN that defines the routing of traffic to the appropriate target group.
In Target Group Tuples, specify:
-
Target Group ARN: Select the target group to which traffic should be shifted.
-
Weight: Specify the weight to be associated with the target group in the listener rule.
For details on how weights work and supported values, refer to the AWS ALB Listener Rule documentation.
You can provide one or more Target Group Tuples, and the forward configuration for the listener rule will be set accordingly based on the weights specified in each tuple.
If only one Target Group Tuple is provided, 100% of the traffic will be routed to the specified Target Group ARN for the listener rule.
Sample YAML of the step group
Sample YAML
- step:
identifier: ElastigroupBlueGreenTrafficShift
type: ElastigroupBlueGreenTrafficShift
name: Stage rule Shift
timeout: 10m
spec:
elastigroupTrafficShiftWrapper:
type: Standalone
spec:
loadBalancer: namanSpot
listenerArn: <+stage.variables.devListener>
listenerRuleArn: <+stage.variables.stageRule>
forwardTrafficConfig:
- targetGroupArn: <+stage.variables.stageTargetGroup>
weight: <+matrix.weight>
- targetGroupArn: <+stage.variables.prodTargetGroup>
weight: <+(100 - <+matrix.weight>)>
The Standalone step does not perform any renaming of the associated Spot Elastigroup services, regardless of the traffic weight specified.
Rollback Behavior
When you run the Elastigroup Blue-Green Traffic Shifting step, the system stores the initial configuration as Prepare Rollback Data before execution begins.
-
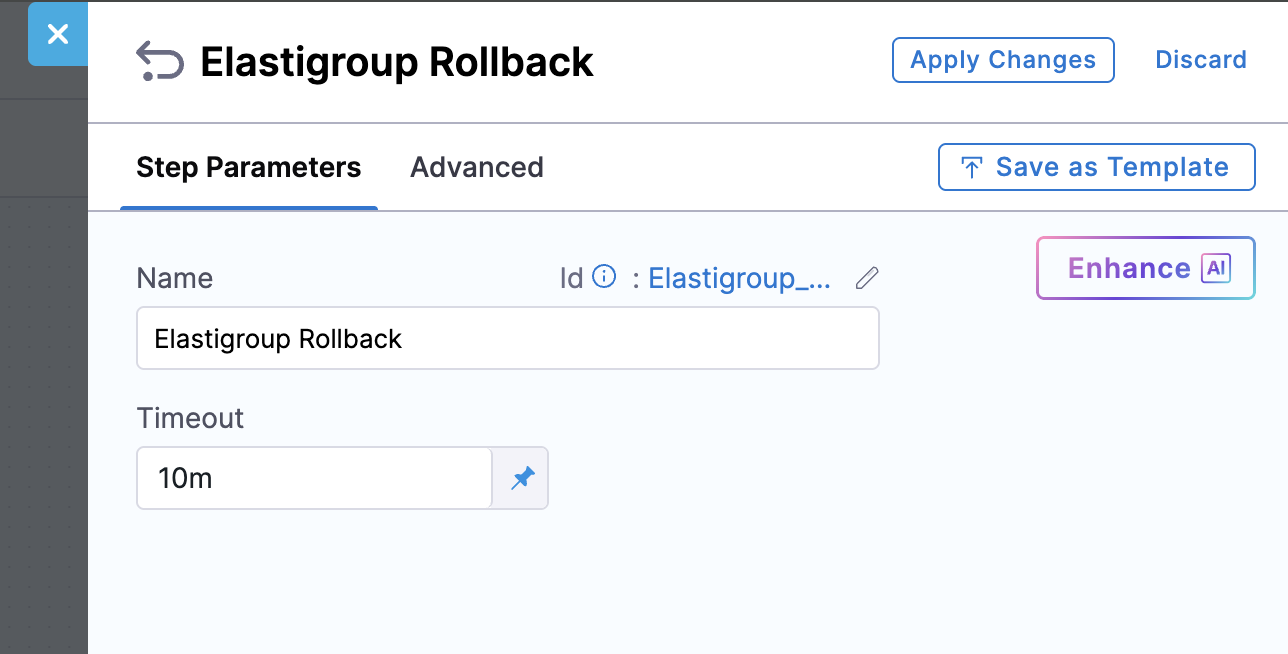
In Inherit mode, if the step fails mid-execution, the rollback is handled by the Elastigroup Rollback step, which restores the traffic weights and names of the Elastigroups using the stored rollback data.
-
In Standalone mode, during the first execution of each listener rule, the system captures the original forward configuration as part of the rollback data. If a failure occurs, the Standalone Traffic Shift Rollback step restores the original forward configuration for all affected listener rules.
In both cases, rollback steps ensure that traffic is routed back to the original setup in the event of a failure.
Rollback behavior depends on the mode used:
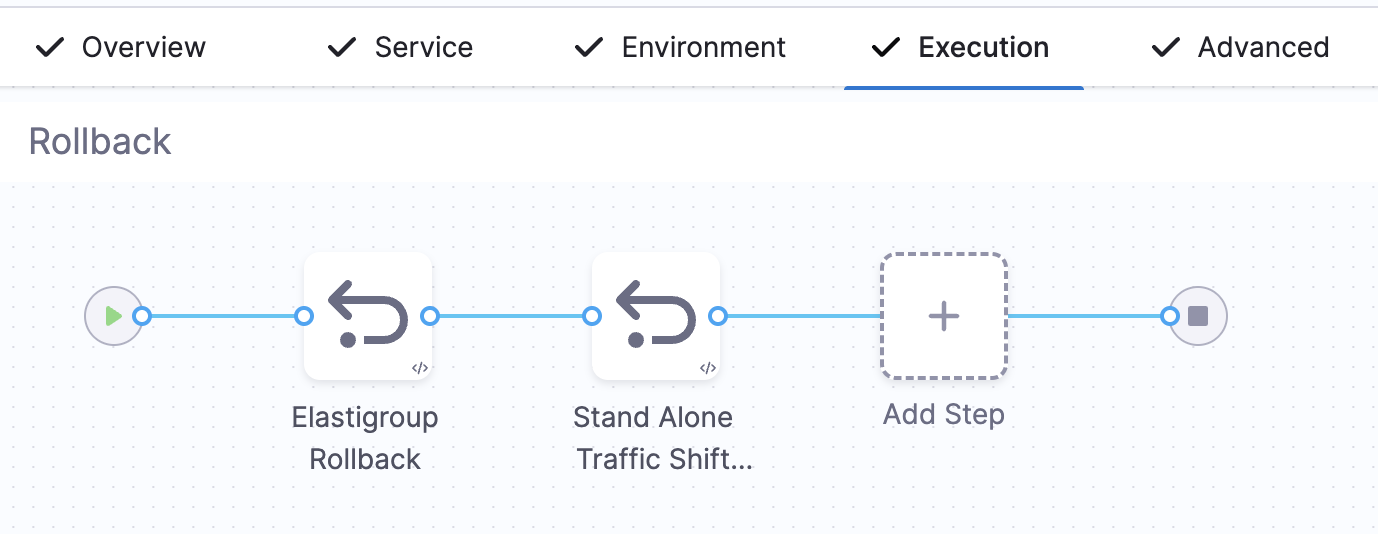
- Inherit Mode: Restores the initial traffic weights using the Elastigroup Rollback step.
- Standalone Mode: Resets the original forward configuration for all listener rules used in the stage using the Standalone Traffic Shift Rollback step.
In both cases, the original forward configuration is restored in the event of a failure or rollback trigger, using the appropriate rollback step for each mode.
Limitations
- For supported target group weights and configuration options, refer to the AWS ALB Listener Rules documentation.
- Maximum of 5 target groups per rule (AWS limitation).
- Auto Scaling during swap is not supported.
The Swap step can be used alongside the Traffic Shift step in the same stage, especially in scenarios with multiple load balancer configurations.
General Solution Pattern for Traffic Shifting
For customers who want to implement progressive traffic shifting (e.g., 10% → 30% → 100%) across environments:
- Attach two target groups to a single ALB listener rule designated as the production rule.
- Create a separate listener rule for the dev environment that uses the same two target groups.
- In the Elastigroup Blue-Green Traffic Shifting step, specify the production listener rule.
- In lower environments, shift traffic to the stage target group using the Standalone Traffic Shift step with the dev listener rule.
- In production, use Inherit mode to gradually increase traffic to the new service version via the stage target group.
- Use Elastigroup Traffic Shift steps to adjust traffic incrementally (e.g., 10%, 50%, 100%) with optional approval gates between shifts.
- When traffic reaches 100%, the associated Spot Elastigroup is renamed to the App Name specified in the Blue-Green Traffic Shift step.
Comparison: Traditional Blue-Green vs. Traffic Shifting
Traditional Blue-Green Deployment (Pre-Traffic Shifting)
- Requires two separate listener rules (typically configured on different ports)
- New version is deployed to the Stage target group associated with a different listener rule (commonly mapped to a separate port)
- After manual/automated validation, a Swap Target Groups step is used to direct 100% traffic to the new version
- You cannot test the new version on live production traffic until after the swap
- Swap is atomic—no gradual rollout or partial traffic shift
Blue-Green Deployment with Traffic Shifting (New Flow)
- Uses a single listener rule with weighted target groups
- New version is deployed to a target group under the same listener rule as the old version
- Allows progressive traffic rollout (e.g., 10% → 50% → 100%) using Elastigroup Traffic Shift step
- Eliminates need for separate ports or manual AWS CLI scripts
- Enables staged rollout with approval gates, monitoring, and rollback safety
- No Swap step needed—transition to full traffic is handled by adjusting target group weights
Note: This new traffic-shifting approach makes Blue-Green deployments safer, more controlled, and production-traffic-aware.
Example Use Case: Controlled Traffic Shifting Across Environments
You can use Elastigroup traffic shifting to gradually roll out and validate a new version of your service across different environments before promoting it to production:
- Deploy the new version of the service once and attach it to the Stage Target Group.
- Keep the prod target group mapped to the existing (old) service.
- In lower environments, incrementally shift traffic to the new service version and validate using CV (Continuous Verification), approval steps, or custom scripts.
- When 100% of the traffic is shifted, the new service is renamed to match the configured App Name.
Example Use Case: Step-by-Step Flow for Gradual Traffic Shifting
This example outlines the basic flow you can follow when implementing Elastigroup Blue-Green deployments with traffic shifting:
- Add the Elastigroup Blue-Green Traffic Shifting step with
isTrafficShift: trueand provide thestageTargetGroupArn. - Add an Elastigroup Blue Green Traffic step (inherit or standalone) to begin shifting traffic incrementally.
- (Optional) Add an approval step to control progression between shifts.
- Repeat the **Elastigroup Blue Green Traffic ** steps to gradually increase traffic to 100%.